With the rise of artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things, businesses in all sectors are redefining how they use the software. Industrial units are learning how their data to predict, prevent, and avoid machine downtime in manufacturing.
Maintenance is a key area that can drive significant cost-saving and production value in manufacturing. According to a report by Deloitte, a poor maintenance strategy can reduce the overall plant’s productivity by 20%, and unplanned downtime can cost $50 billion USD to the manufacturers. Thus, it is crucial to prevent unplanned downtime for maintaining optimum operational efficiency.
Let’s understand first about downtime in manufacturing.
What is downtime in manufacturing?
Downtime in production, particularly in manufacturing, refers to the period during which production activities are halted or interrupted. This interruption encompasses both planned downtime, which occurs for scheduled equipment maintenance or adjustments, and unplanned downtime, which arises from unexpected factors such as equipment malfunctions, shortages of raw materials, or labor strikes.
Over the years, the industries have overhauled maintenance processes to alleviate downtime and improve effectiveness. However, artificial intelligence is the best way to use and analyze data for preventing downtime using a predictive maintenance solution.
With artificial intelligence and machine learning, businesses can process a huge amount of sensor data quicker than ever before. It gives industrial units an unusual option to improve the current sustenance operations and even add maintenance techniques like predictive maintenance.
Manufacturing is thus one of the top industries that can see unprecedented savings by using artificial intelligence. Let’s take a look at how AI can help manufacturers avoid unplanned downtime and enhance the plant’s overall productivity.
How AI can prevent downtime in manufacturing?
Predictive maintenance
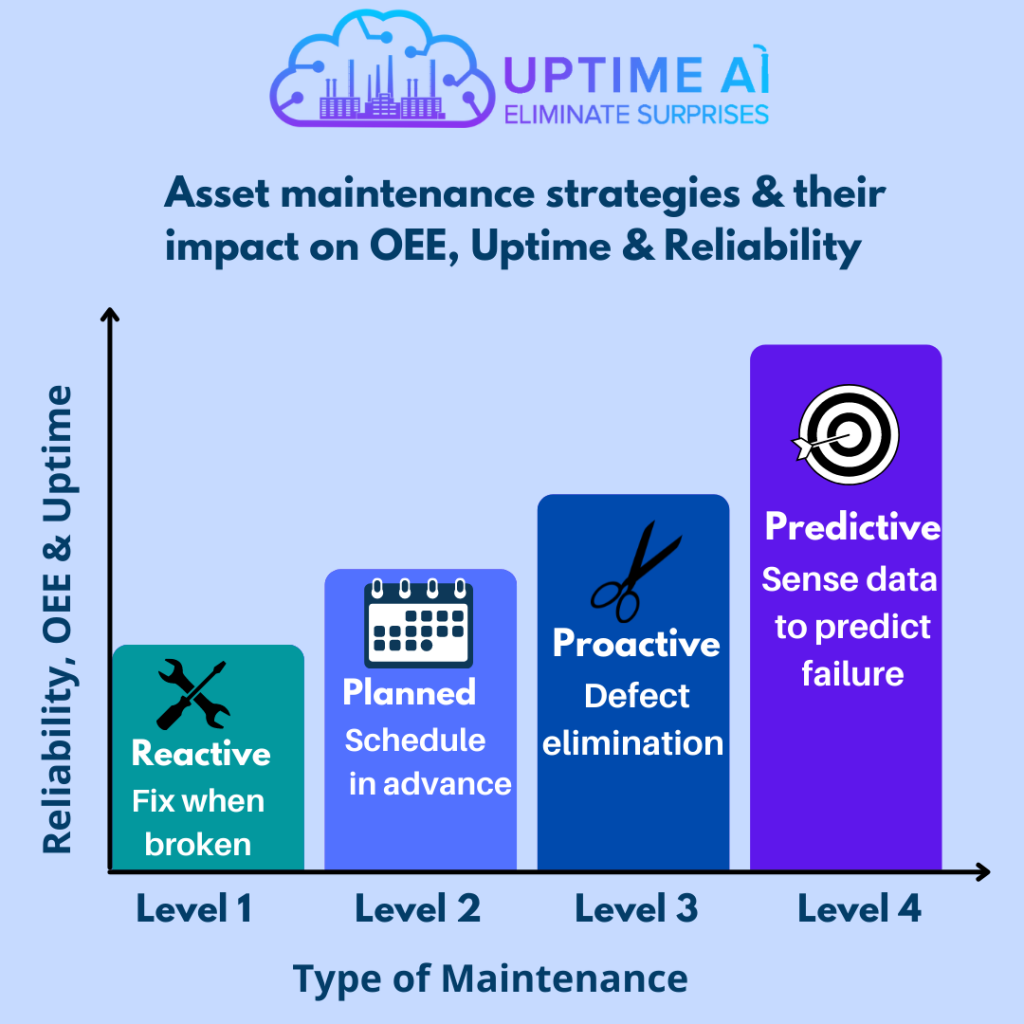
Keeping up and running the manufacturing plant is costly and time-consuming. Besides, it runs a high risk of equipment failure, taking an enormous hit on the production schedule and decreasing productivity. However, predicting when a machine is likely to fail long before it happens is the most important way to avoid downtime.
With help of AI, unplanned downtime is preventable with predictive maintenance. The manufacturers can make an asset viability protection plan, identifying when it will be the most viable to upgrade the plant by responding to the alerts and resolving minor issues.
AI interprets shifts in real-time data & detects anomalies between millions of data points. In seconds, it can detect the previous unknown process, products and workflow by leveraging various data types.
The sensor data is gathered from the equipment itself, detecting movements, heat, vibrations, data track machine outputs and inputs and logic controller. Furthermore, cameras are installed in some cases to capture visual data and time-series data to determine the machine’s state based on its history.
Thus, predictive maintenance is one of the most advanced ways to care for your plants and machinery. Predictive maintenance comes when the artificial intelligence predicts the replacement of the parts before an outage occurs. You can avoid downtime before it arises. It ensures that the production does not stop by preventing equipment failure.
Value-added benefits
Artificial intelligence enables the equipment to gather data from disparate tools, learn and adapt new things and acknowledge patterns through machine learning and speech recognition. By using AI, manufacturers will be able to,
- Make informed decisions
- Advance process effectiveness
- Facilitate superior scalability
- Consistent production outcomes
- Facilitate product development
- Minimize operational cost
Is AI the Future of Manufacturing?
As stated above, the benefits of using artificial learning models in the manufacturing industries are prominent. Predicting potential machine failures that need maintenance can enable industries to handle problems before they arise. This will ultimately save time and money in the long run and enable them to focus on maximum production and decreasing downtime in production.
Conclusion
There is still a lot of work to be done when integrating artificial intelligence with manufacturing equipment. Artificial intelligence may be efficient in maintaining things, improving them and making them affordable. Still, there is no replacement for human ingenuity in dealing with the unanticipated changes in demands and preferences and in deciding whether to make things at all.
But the ultimate goal of utilizing AI in production is not to replace humans but rather to free up their time to focus on more strategic and value-added tasks. AI is the future, and although it is considered a competitive advantage now, the adoption rate of these tools is booming and will soon saturate the entire manufacturing sector.
Need more details to know how we can reduce your unplanned downtime? Book a demo with us at info@uptimeai.com.
FAQs
- What causes manufacturing downtime?
Several factors can contribute to manufacturing downtime. This includes planned downtime for scheduled maintenance and unplanned downtime due to labor strikes, unforeseen accidents and shortage of raw material.
- How is Manufacturing downtime calculated?
You can get the accurate manufacturing downtime by deducting the actual operating time from the planned operating time. The ampere-hours then divided the total number of units produced by the actual operating time to get the average downtime of equipment.
- How can Manufacturing downtime be reduced?
Manufacturing downtime can be reduced by properly evaluating equipment through regular inspection, implementing preventive and predictive methods, timely upgrading equipment and tacking downtime.
- How does downtime affect production?
The downtime in manufacturing affects production in many ways. Due to downtime, the plant remains unoperated, decreasing the number of units produced while the labor and operational costs remain the same. This ultimately results in a low-profit margin for the manufacturing unit.
